इस ट्यूटोरियल में, आप जानेंगे कि एवल ट्री क्या है। इसके अलावा, आप C, C ++, जावा और पायथन में एक एवल ट्री पर किए गए विभिन्न ऑपरेशनों के काम के उदाहरण पाएंगे।
एवीएल पेड़ एक स्व-संतुलन द्विआधारी खोज पेड़ है जिसमें प्रत्येक नोड अतिरिक्त जानकारी रखता है जिसे संतुलन कारक कहा जाता है जिसका मूल्य -1, 0 या 1 है।
एवीएल पेड़ को इसका नाम इसके आविष्कारक जियोरी एडेलसन-वेल्स्की और लैंडिस के नाम पर मिला।
बैलेंस फैक्टर
AVL ट्री में नोड का बैलेंस फैक्टर लेफ्ट सबट्री की ऊंचाई और उस नोड के राइट सबट्री के बीच का अंतर होता है।
बैलेंस फैक्टर = (राइट सबट्री की ऊँचाई - राइट सबट्री की ऊँचाई) या (राइट सबट्री की ऊँचाई - लेफ्ट सबट्री की ऊँचाई)
एक हिमस्खलन पेड़ की आत्म संतुलन संपत्ति संतुलन कारक द्वारा बनाए रखा जाता है। बैलेंस फैक्टर का मान हमेशा -1, 0 या +1 होना चाहिए।
संतुलित एवल ट्री का एक उदाहरण है:
 आँवला का पेड़
आँवला का पेड़
एक एवीएल पेड़ पर संचालन
विभिन्न ऑपरेशन जो एवीएल पेड़ पर किए जा सकते हैं, वे हैं:
एक एवीएल ट्री में उपप्रकार घुमाते हुए
रोटेशन ऑपरेशन में, एक उपप्रकार के नोड्स के स्थान परस्पर जुड़े होते हैं।
घुमाव दो प्रकार के होते हैं:
लेफ्ट रोटेट
बाएं-रोटेशन में, दाएं तरफ नोड्स की व्यवस्था बाएं नोड पर व्यवस्था में तब्दील हो जाती है।
कलन विधि
- प्रारंभिक पेड़ होने दें:
 बाएं घुमाएं
बाएं घुमाएं - यदि y में बाईं सबट्री है, तो x को y के बाएं सबट्री के माता-पिता के रूप में असाइन करें।
 X को y के बाएँ उप-भाग के जनक के रूप में असाइन करें
X को y के बाएँ उप-भाग के जनक के रूप में असाइन करें - यदि x का जनक
NULL, वृक्ष की जड़ के रूप में y बनाते हैं। - और यदि x, p का बांया बच्चा है, तो y को p के बायें बच्चे के रूप में बनाएँ।
- Else y के सही बच्चे के रूप में y असाइन करें।
 Y के x के जनक को बदलें
Y के x के जनक को बदलें - Y को x का जनक बनाएं।
 Y को x के जनक के रूप में असाइन करें।
Y को x के जनक के रूप में असाइन करें।
राइट रोटेट
बाएं-रोटेशन में, बाईं ओर नोड्स की व्यवस्था सही नोड पर व्यवस्थाओं में बदल जाती है।
- शुरुआती पेड़ होने दें:
 प्रारंभिक पेड़
प्रारंभिक पेड़ - यदि x में सही सबट्री है, तो x के राइट सबट्री के अभिभावक के रूप में y असाइन करें।
 Y को x के सही उप-वर्ग के जनक के रूप में असाइन करें
Y को x के सही उप-वर्ग के जनक के रूप में असाइन करें - यदि y का माता-पिता है
NULL, तो x को पेड़ की जड़ बनाएं। - इसके अलावा अगर y उसके माता-पिता का सही बच्चा है, तो x को p के सही बच्चे के रूप में बनाएं।
- El p के बाएं बच्चे के रूप में x असाइन करें।
 X के माता-पिता के रूप में y के माता-पिता को असाइन करें।
X के माता-पिता के रूप में y के माता-पिता को असाइन करें। - X को y के जनक के रूप में बनाएँ।
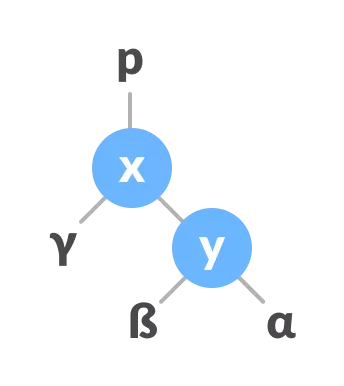 Y के माता-पिता के रूप में x असाइन करें
Y के माता-पिता के रूप में x असाइन करें
लेफ्ट-राइट और राइट-लेफ्ट रोटेट
बाएं-दाएं रोटेशन में, व्यवस्थाएं पहले बाईं ओर और फिर दाईं ओर स्थानांतरित की जाती हैं।
- Xy पर बाएं घूमें।
 लेफ्ट रोटेट एक्स
लेफ्ट रोटेट एक्स - Yz पर दायाँ रोटेशन करें।
 राइट रोट ज़ी
राइट रोट ज़ी
दाएं-बाएं रोटेशन में, व्यवस्थाएं पहले दाएं और फिर बाईं ओर स्थानांतरित की जाती हैं।
- Xy पर राइट रोटेशन करें।
 राइट घुमाएं Xy
राइट घुमाएं Xy - ज़ी पर घूमना छोड़ दें।
 लेफ्ट रोट ज़ाइ
लेफ्ट रोट ज़ाइ
नया नोट डालने के लिए एल्गोरिथम
एक नया नोट हमेशा 0 के बराबर बैलेंस फैक्टर वाले लीफ नोड के रूप में डाला जाता है।
- प्रारंभिक पेड़ होने दें:
 सम्मिलन के लिए प्रारंभिक पेड़
सम्मिलन के लिए प्रारंभिक पेड़
। नोड को सम्मिलित होने दें: नया नोड
नया नोड - निम्नलिखित पुनरावर्ती चरणों का उपयोग करके एक नया नोड सम्मिलित करने के लिए उपयुक्त लीफ नोड पर जाएं। वर्तमान पेड़ के rootKey के साथ newKey की तुलना करें।
- यदि newKey <rootKey, पत्ती के नोड तक पहुंचने तक वर्तमान नोड के बाईं ओर पर सम्मिलन एल्गोरिथ्म को कॉल करें।
- और अगर newKey> rootKey, लीफ नोड तक पहुंचने तक करंट नोड के राइट सबट्री पर इंसर्शन अल्गोरिदम को कॉल करें।
- एल्स, रिटर्न लीफNode।
 NewNode सम्मिलित करने के लिए स्थान ढूँढना
NewNode सम्मिलित करने के लिए स्थान ढूँढना
- नए चरणों के साथ उपरोक्त चरणों से प्राप्त लीफ की तुलना करें:
- यदि newKey <लीफकेय, newNode को लीफकोड के बायीं ओर बनाएं।
- एल्स, न्यूएनोड को राइट-चाइल्ड ऑफ लीफ नॉनडे बनाते हैं।
 नया नोड सम्मिलित करना
नया नोड सम्मिलित करना
- नोड्स के अद्यतन को संतुलित करें।
 प्रविष्टि के बाद संतुलन कारक को अद्यतन करना
प्रविष्टि के बाद संतुलन कारक को अद्यतन करना - यदि नोड्स असंतुलित हैं, तो नोड को फिर से संतुलित करें।
- यदि बैलेंसफैक्टर> 1, इसका मतलब है कि बाएं सबट्री की ऊंचाई सही सबट्री से अधिक है। तो, एक दाएँ रोटेशन या बाएँ-दाएँ रोटेशन करें
- यदि newNodeKey <leftChildKey सही रोटेशन करते हैं।
- और, बाएं-दाएं रोटेशन करें।
 पेड़ को रोटेशन के साथ
पेड़ को रोटेशन के साथ 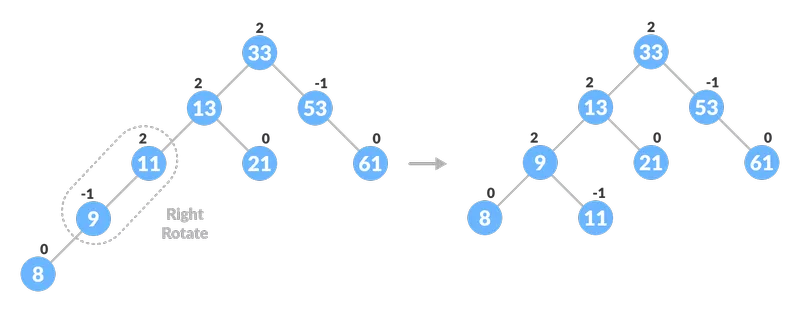 संतुलित करना पेड़ को रोटेशन के साथ संतुलित करना
संतुलित करना पेड़ को रोटेशन के साथ संतुलित करना
- यदि बैलेंसफैक्टर <-1, इसका मतलब है कि सही सबट्री की ऊंचाई बाएं सबट्री से अधिक है। तो, दाएं रोटेशन या दाएं-बाएं रोटेशन करें
- यदि newNodeKey> rightChildKey बाएं घूमता है।
- वरना, दाएं-बाएं घुमाएं
- यदि बैलेंसफैक्टर> 1, इसका मतलब है कि बाएं सबट्री की ऊंचाई सही सबट्री से अधिक है। तो, एक दाएँ रोटेशन या बाएँ-दाएँ रोटेशन करें
- अंतिम पेड़ है:
 अंतिम संतुलित पेड़
अंतिम संतुलित पेड़
नोड को हटाने के लिए एल्गोरिथम
एक नोड को हमेशा लीफ नोड के रूप में हटा दिया जाता है। एक नोड को हटाने के बाद, नोड्स के संतुलन कारक बदल जाते हैं। संतुलन कारक को पुनर्संतुलित करने के लिए, उपयुक्त घुमाव किए जाते हैं।
- पता लगाएँ नोडट्यूबलेट (पुनर्संरचना का उपयोग नीचे दिए गए कोड में नोडटॉयबीडलेट खोजने के लिए किया जाता है)।
 हटाए जा रहे नोड का पता लगाना
हटाए जा रहे नोड का पता लगाना - नोड को हटाने के लिए तीन मामले हैं:
- यदि नोडटॉबलेटेड लीफ नोड है (अर्थात कोई बच्चा नहीं है), तो नोडटोबेलेट हटा दें।
- यदि नोडटॉबलेट में एक बच्चा है, तो नोडटोब की सामग्री को बच्चे के साथ प्रतिस्थापित करें। बच्चे को निकालो।
- यदि नोडटबबलेटेड में दो बच्चे हैं, तो नोडटॉयबेडलेट के इनवर्टर उत्तराधिकारी डब्ल्यू को खोजें (यानी सही उपट में कुंजी का न्यूनतम मान के साथ नोड)।
 उत्तराधिकारी का पता लगाना
उत्तराधिकारी का पता लगाना
- नोड की सामग्री को उसी के साथ हटा दें।
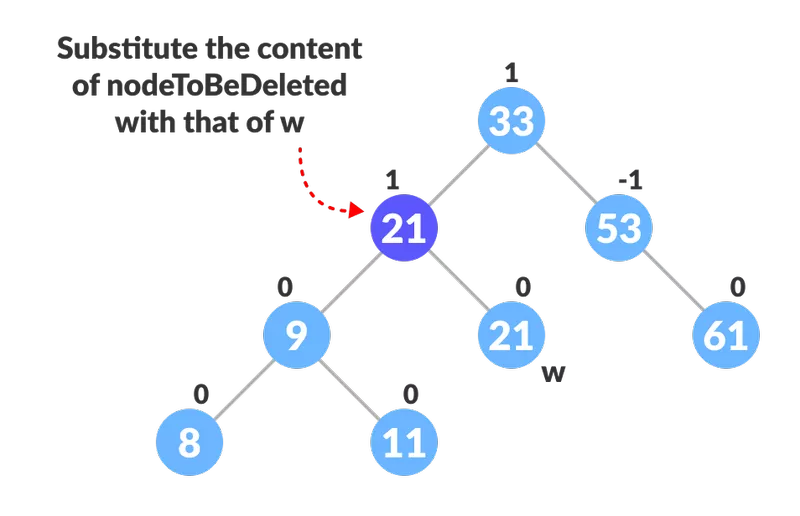 हटाए जाने के लिए नोड को प्रतिस्थापित करें
हटाए जाने के लिए नोड को प्रतिस्थापित करें - पत्ती नोड डब्ल्यू निकालें।
 W को हटा दें
W को हटा दें
- नोड की सामग्री को उसी के साथ हटा दें।
- नोड्स के अद्यतन को संतुलित करें।
 अद्यतन bf
अद्यतन bf - यदि किसी भी नोड का संतुलन कारक -1, 0 या 1 के बराबर नहीं है, तो पेड़ को असंतुलित करें।
- यदि संतुलन की वर्तमान धारा 1,
- यदि बायाँ गढ़ का संतुलन> = 0, दाएं रोटेशन करें।
 पेड़ को संतुलित करने के लिए राइट-रोटेट करें
पेड़ को संतुलित करने के लिए राइट-रोटेट करें - एल्स बायें-दायें घूमते हैं।
- यदि बायाँ गढ़ का संतुलन> = 0, दाएं रोटेशन करें।
- यदि बैलेंस करेंटियरनोड का वर्तमान <-1,
- अगर संतुलन सही है दाहिने <= 0, तो बाएं रोटेशन करें।
- वरना दायें-बायें घूमते हैं।
- यदि संतुलन की वर्तमान धारा 1,
- अंतिम वृक्ष है:
 अवल वृक्ष अंतिम
अवल वृक्ष अंतिम
पायथन, जावा और सी / सी ++ उदाहरण
पायथन जावा सी सी ++ # AVL tree implementation in Python import sys # Create a tree node class TreeNode(object): def __init__(self, key): self.key = key self.left = None self.right = None self.height = 1 class AVLTree(object): # Function to insert a node def insert_node(self, root, key): # Find the correct location and insert the node if not root: return TreeNode(key) elif key 1: if key < root.left.key: return self.rightRotate(root) else: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root) if balanceFactor root.right.key: return self.leftRotate(root) else: root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root # Function to delete a node def delete_node(self, root, key): # Find the node to be deleted and remove it if not root: return root elif key root.key: root.right = self.delete_node(root.right, key) else: if root.left is None: temp = root.right root = None return temp elif root.right is None: temp = root.left root = None return temp temp = self.getMinValueNode(root.right) root.key = temp.key root.right = self.delete_node(root.right, temp.key) if root is None: return root # Update the balance factor of nodes root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) balanceFactor = self.getBalance(root) # Balance the tree if balanceFactor> 1: if self.getBalance(root.left)>= 0: return self.rightRotate(root) else: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root) if balanceFactor < -1: if self.getBalance(root.right) <= 0: return self.leftRotate(root) else: root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root # Function to perform left rotation def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left y.left = z z.right = T2 z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) return y # Function to perform right rotation def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right y.right = z z.left = T3 z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) return y # Get the height of the node def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height # Get balance factore of the node def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def getMinValueNode(self, root): if root is None or root.left is None: return root return self.getMinValueNode(root.left) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print("(0) ".format(root.key), end="") self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Print the tree def printHelper(self, currPtr, indent, last): if currPtr != None: sys.stdout.write(indent) if last: sys.stdout.write("R----") indent += " " else: sys.stdout.write("L----") indent += "| " print(currPtr.key) self.printHelper(currPtr.left, indent, False) self.printHelper(currPtr.right, indent, True) myTree = AVLTree() root = None nums = (33, 13, 52, 9, 21, 61, 8, 11) for num in nums: root = myTree.insert_node(root, num) myTree.printHelper(root, "", True) key = 13 root = myTree.delete_node(root, key) print("After Deletion: ") myTree.printHelper(root, "", True)
// AVL tree implementation in Java // Create node class Node ( int item, height; Node left, right; Node(int d) ( item = d; height = 1; ) ) // Tree class class AVLTree ( Node root; int height(Node N) ( if (N == null) return 0; return N.height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) Node rightRotate(Node y) ( Node x = y.left; Node T2 = x.right; x.right = y; y.left = T2; y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1; x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1; return x; ) Node leftRotate(Node x) ( Node y = x.right; Node T2 = y.left; y.left = x; x.right = T2; x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1; y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get balance factor of a node int getBalanceFactor(Node N) ( if (N == null) return 0; return height(N.left) - height(N.right); ) // Insert a node Node insertNode(Node node, int item) ( // Find the position and insert the node if (node == null) return (new Node(item)); if (item node.item) node.right = insertNode(node.right, item); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node // And, balance the tree node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (item node.left.item) ( node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(node); ) ) if (balanceFactor node.right.item) ( return leftRotate(node); ) else if (item < node.right.item) ( node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); ) ) return node; ) Node nodeWithMimumValue(Node node) ( Node current = node; while (current.left != null) current = current.left; return current; ) // Delete a node Node deleteNode(Node root, int item) ( // Find the node to be deleted and remove it if (root == null) return root; if (item root.item) root.right = deleteNode(root.right, item); else ( if ((root.left == null) || (root.right == null)) ( Node temp = null; if (temp == root.left) temp = root.right; else temp = root.left; if (temp == null) ( temp = root; root = null; ) else root = temp; ) else ( Node temp = nodeWithMimumValue(root.right); root.item = temp.item; root.right = deleteNode(root.right, temp.item); ) ) if (root == null) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and balance the tree root.height = max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1; int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(root); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root.left)>= 0) ( return rightRotate(root); ) else ( root.left = leftRotate(root.left); return rightRotate(root); ) ) if (balanceFactor < -1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root.right) <= 0) ( return leftRotate(root); ) else ( root.right = rightRotate(root.right); return leftRotate(root); ) ) return root; ) void preOrder(Node node) ( if (node != null) ( System.out.print(node.item + " "); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); ) ) // Print the tree private void printTree(Node currPtr, String indent, boolean last) ( if (currPtr != null) ( System.out.print(indent); if (last) ( System.out.print("R----"); indent += " "; ) else ( System.out.print("L----"); indent += "| "; ) System.out.println(currPtr.item); printTree(currPtr.left, indent, false); printTree(currPtr.right, indent, true); ) ) // Driver code public static void main(String() args) ( AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 33); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 13); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 53); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 9); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 21); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 61); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 8); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 11); tree.printTree(tree.root, "", true); tree.root = tree.deleteNode(tree.root, 13); System.out.println("After Deletion: "); tree.printTree(tree.root, "", true); ) )
// AVL tree implementation in C #include #include // Create Node struct Node ( int key; struct Node *left; struct Node *right; int height; ); int max(int a, int b); // Calculate height int height(struct Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return N->height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) // Create a node struct Node *newNode(int key) ( struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->key = key; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; node->height = 1; return (node); ) // Right rotate struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y) ( struct Node *x = y->left; struct Node *T2 = x->right; x->right = y; y->left = T2; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; return x; ) // Left rotate struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x) ( struct Node *y = x->right; struct Node *T2 = y->left; y->left = x; x->right = T2; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get the balance factor int getBalance(struct Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return height(N->left) - height(N->right); ) // Insert node struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int key) ( // Find the correct position to insertNode the node and insertNode it if (node == NULL) return (newNode(key)); if (key key) node->left = insertNode(node->left, key); else if (key> node->key) node->right = insertNode(node->right, key); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node and // Balance the tree node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); int balance = getBalance(node); if (balance> 1 && key left->key) return rightRotate(node); if (balance node->right->key) return leftRotate(node); if (balance> 1 && key> node->left->key) ( node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); ) if (balance < -1 && key right->key) ( node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); ) return node; ) struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node) ( struct Node *current = node; while (current->left != NULL) current = current->left; return current; ) // Delete a nodes struct Node *deleteNode(struct Node *root, int key) ( // Find the node and delete it if (root == NULL) return root; if (key key) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); else if (key> root->key) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); else ( if ((root->left == NULL) || (root->right == NULL)) ( struct Node *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; if (temp == NULL) ( temp = root; root = NULL; ) else *root = *temp; free(temp); ) else ( struct Node *temp = minValueNode(root->right); root->key = temp->key; root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key); ) ) if (root == NULL) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree root->height = 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right)); int balance = getBalance(root); if (balance> 1 && getBalance(root->left)>= 0) return rightRotate(root); if (balance> 1 && getBalance(root->left) left = leftRotate(root->left); return rightRotate(root); ) if (balance right) <= 0) return leftRotate(root); if (balance right)> 0) ( root->right = rightRotate(root->right); return leftRotate(root); ) return root; ) // Print the tree void printPreOrder(struct Node *root) ( if (root != NULL) ( printf("%d ", root->key); printPreOrder(root->left); printPreOrder(root->right); ) ) int main() ( struct Node *root = NULL; root = insertNode(root, 2); root = insertNode(root, 1); root = insertNode(root, 7); root = insertNode(root, 4); root = insertNode(root, 5); root = insertNode(root, 3); root = insertNode(root, 8); printPreOrder(root); root = deleteNode(root, 3); printf("After deletion: "); printPreOrder(root); return 0; )
// AVL tree implementation in C++ #include using namespace std; class Node ( public: int key; Node *left; Node *right; int height; ); int max(int a, int b); // Calculate height int height(Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return N->height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) // New node creation Node *newNode(int key) ( Node *node = new Node(); node->key = key; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; node->height = 1; return (node); ) // Rotate right Node *rightRotate(Node *y) ( Node *x = y->left; Node *T2 = x->right; x->right = y; y->left = T2; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; return x; ) // Rotate left Node *leftRotate(Node *x) ( Node *y = x->right; Node *T2 = y->left; y->left = x; x->right = T2; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get the balance factor of each node int getBalanceFactor(Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return height(N->left) - height(N->right); ) // Insert a node Node *insertNode(Node *node, int key) ( // Find the correct postion and insert the node if (node == NULL) return (newNode(key)); if (key key) node->left = insertNode(node->left, key); else if (key> node->key) node->right = insertNode(node->right, key); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (key left->key) ( return rightRotate(node); ) else if (key> node->left->key) ( node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); ) ) if (balanceFactor node->right->key) ( return leftRotate(node); ) else if (key right->key) ( node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); ) ) return node; ) // Node with minimum value Node *nodeWithMimumValue(Node *node) ( Node *current = node; while (current->left != NULL) current = current->left; return current; ) // Delete a node Node *deleteNode(Node *root, int key) ( // Find the node and delete it if (root == NULL) return root; if (key key) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); else if (key> root->key) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); else ( if ((root->left == NULL) || (root->right == NULL)) ( Node *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; if (temp == NULL) ( temp = root; root = NULL; ) else *root = *temp; free(temp); ) else ( Node *temp = nodeWithMimumValue(root->right); root->key = temp->key; root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key); ) ) if (root == NULL) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree root->height = 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(root); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root->left)>= 0) ( return rightRotate(root); ) else ( root->left = leftRotate(root->left); return rightRotate(root); ) ) if (balanceFactor right) right = rightRotate(root->right); return leftRotate(root); ) ) return root; ) // Print the tree void printTree(Node *root, string indent, bool last) ( if (root != nullptr) ( cout << indent; if (last) ( cout << "R----"; indent += " "; ) else ( cout << "L----"; indent += "| "; ) cout right, indent, true); ) ) int main() ( Node *root = NULL; root = insertNode(root, 33); root = insertNode(root, 13); root = insertNode(root, 53); root = insertNode(root, 9); root = insertNode(root, 21); root = insertNode(root, 61); root = insertNode(root, 8); root = insertNode(root, 11); printTree(root, "", true); root = deleteNode(root, 13); cout << "After deleting " << endl; printTree(root, "", true); )
एक AVL ट्री पर विभिन्न प्रचालनों की जटिलताएँ
| सम्मिलन | नष्ट करना | खोज |
| O (लॉग एन) | O (लॉग एन) | O (लॉग एन) |
एवीएल ट्री एप्लीकेशन
- डेटाबेस में बड़े रिकॉर्ड्स को अनुक्रमित करने के लिए
- बड़े डेटाबेस में खोज के लिए








